In today’s world, portable power solutions are essential for staying connected and powered up, whether at home, outdoors, or during emergencies. Three common devices—power banks, power stations, and power batteries—are often mentioned in this context, but they serve different purposes and have distinct features. This article introduces each and highlights their differences to help you choose the right solution for your needs.
Introduction:
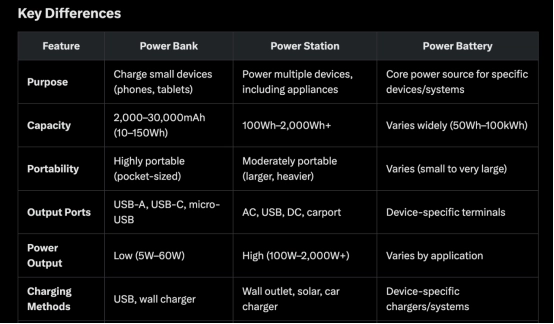
A power bank is a compact, portable device designed to charge small electronic devices like smartphones, tablets, earbuds, or smartwatches. It typically uses a lithium-ion or lithium-polymer battery and is small enough to fit in a pocket or bag.
Key Features:
Capacity: Ranges from 2,000mAh to 30,000mAh, sufficient for charging small devices multiple times.
Ports: Usually equipped with USB-A, USB-C, or micro-USB ports, sometimes with wireless charging capabilities.
Charging: Recharged via USB from a wall adapter, computer, or other power source.
Portability: Lightweight (100g–500g) and pocket-sized for everyday carry.
Use Case: Ideal for daily use, travel, or situations where access to power outlets is limited.
Examples of Use:
Charging a smartphone during a commute.
Powering wireless earbuds on a long flight.
Keeping a tablet running during a workday.

Introduction:
A portable power station is a larger, more powerful device designed to provide electricity for a wide range of devices, including laptops, small appliances, and even medical equipment. It serves as a mini power hub for off-grid or emergency scenarios.
Key Features:
Capacity: Typically ranges from 100Wh to over 2,000Wh, capable of powering high-wattage devices for extended periods.
Ports: Includes AC outlets, USB ports, DC outputs, and sometimes 12V carports or wireless charging pads.
Inverter Technology: Converts DC to AC power, allowing it to run household appliances.
Charging: Rechargeable via wall outlets, solar panels, or car chargers, often supporting multiple methods.
Portability: Heavier (1kg–20kg) but designed with handles for transport; less portable than power banks.
Use Case: Suitable for camping, RV trips, power outages, or off-grid living.
Examples of Use:
Powering a mini fridge during a camping trip.
Running a CPAP machine during a power outage.
Charging laptops and cameras for remote work.

Introduction:
The term "power batteries" is less standardized but generally refers to individual battery cells or packs used as components in various applications, such as electric vehicles (EVs), laptops, or custom power solutions. These are not standalone consumer products like power banks or power stations but rather the core power source within devices or systems.
Key Features:
Types: Commonly lithium-ion, lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO4), or nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), designed for specific applications.
Capacity: Varies widely depending on the application (e.g., 50Wh for laptop batteries, up to 100kWh for EV batteries).
Ports/Connections: Typically lack consumer-facing ports; instead, they connect to devices or systems via specialized terminals or circuits.
Charging: Requires specific chargers or systems (e.g., EV charging stations or device-specific chargers).
Portability: Varies—small for consumer electronics, large and heavy for industrial uses.
Use Case: Found in EVs, drones, power tools, or as replacements for device-specific batteries.
Examples of Use:
Powering an electric vehicle for long-distance travel.
Serving as the battery pack in a cordless drill.
Acting as a replacement battery for a laptop or e-bike

Choosing the Right Option
Power Bank: Best for lightweight, on-the-go charging of small devices. Choose based on capacity (mAh) and port compatibility.
Power Station: Ideal for outdoor adventures, emergencies, or powering larger devices. Consider capacity (Wh), output power (W), and charging options like solar.
Power Battery: Relevant for replacing or upgrading batteries in specific devices or systems. Ensure compatibility with voltage, capacity, and device requirements.
Power banks, power stations, and power batteries each play unique roles in providing portable power. Power banks are perfect for daily convenience, power stations excel in versatile and high-power applications, and power batteries are specialized components for specific devices or systems. Understanding their differences ensures you select the right tool for your power needs, whether for a quick phone charge, a camping trip, or a custom power solution.





